Industries-> Smart Energy


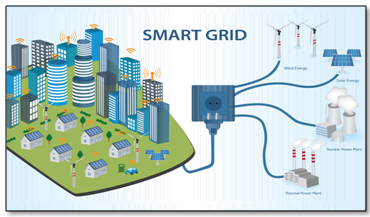
In the dynamic landscape of smart energy, the incorporation of the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing how we generate, distribute, and consume power. At the forefront of this transformation is the implementation of smart grids, where IoT-enabled devices and sensors seamlessly integrate with traditional infrastructure. Smart meters, equipped with IoT technology, offer real-time insights into energy consumption patterns, allowing both utility providers and consumers to make informed decisions about usage and efficiency. The synergy between IoT and smart grids facilitates enhanced grid management, enabling better load balancing, rapid response to fluctuations in demand, and the integration of renewable energy sources. This interconnected ecosystem extends to consumers, empowering them with smart home devices that optimize energy usage, from thermostats that adapt to user preferences to appliances that operate during periods of lower demand. In essence, IoT in smart energy and smart grids converges to create a more responsive, sustainable, and interconnected energy infrastructure for the future.
Benefits of IoT in Energy Efficiency
The benefits of IoT in energy efficiency are numerous. IoT enables real-time monitoring and control of energy consumption, enabling consumers to make informed decisions about their energy use. This, in turn, leads to a reduction in energy waste and a lower carbon footprint. Additionally, IoT can enable the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, making our energy systems more sustainable and resilient.
IoT can also enable the optimization of energy distribution, reducing the need for costly infrastructure upgrades. For instance, utilities can use IoT sensors to monitor the health of the grid and identify potential problems before they become critical, enabling them to perform maintenance and repairs before a failure occurs. This, in turn, leads to a more reliable and resilient grid.
Finally, IoT can enable the creation of new business models and revenue streams. For instance, utilities can offer demand-response programs that enable customers to reduce their energy consumption during periods of high demand in exchange for incentives. This, in turn, leads to a more efficient and cost-effective energy system.
Challenges in Implementing IoT in Energy Efficiency
While the benefits of IoT in energy efficiency are clear, there are several challenges to implementing IoT in energy systems. One of the biggest challenges is the lack of standardization in the industry. Different utilities use different systems and platforms, making it difficult to integrate them with each other. Additionally, there are concerns around cybersecurity, as energy systems are vulnerable to hacking and cyber attacks.
Another challenge is the cost of implementing IoT in energy systems. IoT devices and sensors can be expensive, and the cost of retrofitting existing infrastructure can be prohibitive. Additionally, there are concerns around data privacy, as IoT devices collect large amounts of data that can be sensitive and personal.
IoT Devices for Energy Management
There are several IoT devices and sensors that can be used for energy management. Smart thermostats, for instance, can learn our temperature preferences and adjust the temperature accordingly, thereby reducing energy waste. Smart lighting systems can turn off lights when no one is in the room, saving energy and reducing our carbon footprint. Smart plugs can be used to monitor the energy consumption of individual devices and appliances, enabling us to identify energy hogs and reduce their energy consumption.
Additionally, there are IoT devices and sensors that can be used for energy management at the grid level. Smart meters, for instance, provide real-time information on energy consumption, enabling utilities to optimize their energy distribution and reduce waste. IoT sensors can also be used to monitor the health of the grid and identify potential problems before they become critical.
Future of IoT in Energy Efficiency
The future of IoT in energy efficiency is bright. As the cost of IoT devices and sensors continues to decrease, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of IoT in energy systems. Additionally, as the industry becomes more standardized, we can expect to see greater interoperability between different systems and platforms.
There are also exciting developments on the horizon, such as the use of blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer energy trading. This would enable consumers to buy and sell energy directly to each other, bypassing utilities and reducing the cost of energy.
However, there are also concerns around the potential negative impact of IoT on energy efficiency. For instance, the proliferation of IoT devices and sensors could lead to an increase in energy consumption if they are not properly managed. Additionally, there are concerns around the environmental impact of producing and disposing of IoT devices.


Android Handheld UHF Reader
Automatic Boom Barrier
Automatic Number Plate Reader Camera
Bin Level Sensor
Bio Metrics Machine
Bullet Camera Live
Chlorine Sensor
Data Transmission Unit
Emergency Call Box
Environment Sensor
Face Recognition
Flood Sensor
Fuel Sensor
Galvanized Iron Pole
Gi-Pole
GPS
GPS-AIS140
Handheld HF Reader
Handheld UHF Reader
PTZ Camera
Public Address Speaker
Public Address System
Hydraulic Boom Barrier
IP Bullet Camera
IRIS
Magnetic Sensor
Network Rack
Network Video Recorder
Panic Button
Parking Entry Exit UHF Reader Vehicle Mounted UHF Reader
Passenger information systems
Ph Sensor
Refrigerator Sensor
RFID Tag – HF
RFID Tag – UHF
RFID Tag Metal – UHF
Smart Kiosk
Smart Pole
Soil Sensor
Drainage Sensor
Temperature Sensor
Turbidity Sensor
Ultrasonic Flow Meter Variable Sign Board Weigh Bridge Entry Exit Reader
Ajeevi Offer “Enterprise IoT Solutions” with in-house R&D, Capability of manufacturing IOT devices.
505, Tower A-1, Corporate Park
Noida 201301, Uttar Pradesh India
presales@ajeevi.com
+91-9654323500